 |
Previous: Introduction. Next: First results: VMR maps of the observed species Up: Ext. Abst.
SAFIRE/A operation during the APE-GAIA campaign
SAFIRE-A (Spectroscopy of the Atmosphere using Far-InfraRed Emission / Airborne) [1] is a polarising far infrared Fourier transform (FT) spectrometer operating onboard the M55 Geophysica stratospheric aircraft. In the five scientific flights which the aircraft performed over the Antarctic Peninsula, during the APE-GAIA (Airborne Polar Experiment - Geophysica Aircraft In Antarctica) campaign, the instrument provided limb sounding observations of atmospheric emission spectra over two frequency intervals: [22-23.5 cm-1], and [123-125 cm-1] where spectral features respectively of O3, ClO, N2O, HNO3 and HCl, H2O are displayed. Some of the principal characteristics of the SAFIRE/A instrument are presented in table 1.
| Instrument type | Polarising FTS |
| Dimensions | 1800 x 880 x 650 mm |
| Weight | 387 Kg |
| Observation technique | limb-scanning |
| Acquisition time | 12-24-48-96 s |
| Number of detection channels | 2 |
| Operating spectral range | 10-250 cm-1 |
| Spectral resolution | 0.004 cm-1 |
| Vertical resolution | about 1.5 km |
| Spectral signal-to-noise ratio | >500 |
| Vertical field of view | 0.57o |
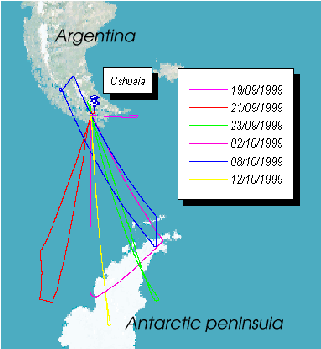
In figure 1 the flight tracks corresponding to each of the scientific flights
performed during the APE-GAIA campaign are shown. The choice of
the Ushuaia international airport as a base for the campaign permitted
to explore the Antarctic polar vortex region, spanning a latitude
range from 58 to about 68 degrees south.
 |
During each flight the SAFIRE/A instrument vertically sampled the atmosphere with limb sounding sequences of 10 emission spectra, corresponding to a vertical resolution of about 1.5 km. The acquisition time for a single spectrum was 30 s, each sequence taking about 5 minutes. This, considering the aircraft average ground speed of 700 km/h at stratospheric altitude, gave an horizontal resolution of about 60 km, corresponding to 0.5 degrees of latitude. The amount of valid data acquired by SAFIRE/A in each flight is given in table 2 as a percentage of the total recorded data.
| Scientific flight | Data acquired | Failure reason |
| 19/9/1999 (test) | 0% | photolitographic BS, aircraft roll |
| 21/9/1999 | 60% | reference laser, roll |
| 23/9/1999 | 90% | roll |
| 2/10/1999 | 30% | roll |
| 8/10/1999 | 100% | - |
| 12/10/1999 | 100% | - |
In figure 2 a typical limb scanning sequence of spectra acquired from the
long wavelength detection channel (22-23.5 cm-1) of the instrument is shown. The simultaneous presence in the
same spectral interval of both chemically active species, like
ozone, HNO3 and ClO and tracers, like N2O permits to obtain a characterization of chemical and dynamical
processes in the lower stratosphere through correlation between
atmospheric components.