Previous: Composite analysis of the upper tropospheric pattern Next: Concluding remarks Up: Ext. Abst.
4. EOF and SVD analysis of the troposphere
In order to confirm the dynamical coupling between the troposphere
and stratosphere in more detail, we applied the EOF and SVD analysis
to the tropospheric zonal winds and 300hPa heat fluxes.
Fig.4a shows the first mode of tropospheric U (TUEOF1, Fraction
of variance 55%), which is the dipole pattern throughout the whole
troposphere, indicating the appearance of single and double jet
structure. The classification by this principal component TUPC1
sign (Fig.4b) confirms the separation of the east-west drift of
the phase of stratospheric waves.
On the other hand, the first component of 300hPa T'v' pattern
(VTEOF1, Fig.5a) reflects the wave activity over the Indian Ocean,
though the fraction of variance is rather weak (9.3%), and the
stratospheric wave intensity is clearly separated by the sign
of TVPC1 (Fig.5b).
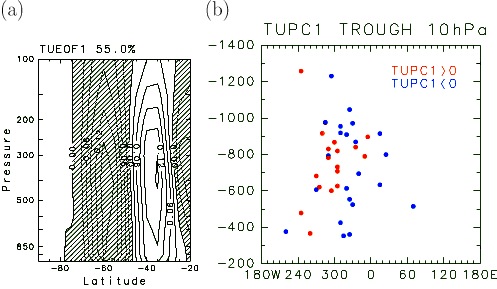
Figure 4 . Latitude height section (1000-100 hPa) of the first
EOF mode for monthly mean zonal wind averaged longitudinally for
the eastern hemisphere, (b) Scatter diagram of the value and the
longitude of the minimum Z* (trough) at 10hPa.
Red (blue) circle denotes the positive (negative) PC1 index for
zonal wind U .
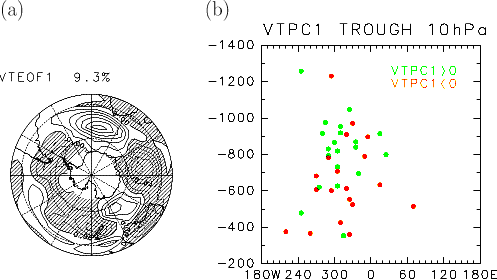
Figure 5 . Same as Fig.4 ,but (a) the first EOF mode for monthly
mean horizontal eddy heat flux at 300 hPa , (b) green (orange)
circle denotes the positive (negative) PC1 index for T'v' .
Furthermore, the result of the SVD analysis for the 10hPa height
field anomaly Z* and 300hPa T'v', though not shown here, shows
that the first and second mode explain the fluctuation of the
phase and amplitude for Z* respectively. The temporal correlation
coefficients between the expansion coefficients is high for the
first two mode.(r=0.78,0.77 ,respectively). This also confirms
the dynamical control of planetary waves in the stratosphere by
the tropospheric transient disturbances.
Previous: Composite analysis of the upper tropospheric pattern Next: Concluding remarks Up: Ext. Abst.

