![[Picture]](SP_lotus.jpg)
Saroja Polavarapu
Adjunct Professor
Department of Physics, University of Toronto
60 St. George Street, Toronto
Ontario,
CANADA M5S 1A7
Tel: (416) 978-xxxx
Fax: (416) 978-8905
E-mail:
saroja@atmosp.physics.utoronto.ca
or
saroja.polavarapu@ec.gc.ca
Atmospheric Physics
Data assimilation; Kalman filtering; Four-Dimensional Variational
Assimilation; Three-Dimensional Variational Assimilation, Optimal
Interpolation; Initialization; gravity wave control with digital
filters.

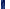
B.Sc., York (1982); M.Sc., Toronto (1984);
Ph.D., Toronto (1989) ; Post-Doctoral Fellow, Meteorological
Service of Canada (1990-1); Research Scientist,
Data Assimilation and Satellite Meteorology Division,
Meteorological Service of Canada (1992-).
Research Interests
Middle Atmosphere Data assimilation for climate applications.
The goal of this work is to combine model forecasts from the
Canadian Middle Atmosphere Model (
CMAM) and available observations
to produce a ``best'' estimate of the atmosphere for climate
diagnostics. The 3-Dimensional Variational (3DVAR) assimilation
scheme used by the
Meteorological Service of Canada (MSC) to produce
operational weather forecasts provides the data assimilation
component. Observations include conventional tropospheric data
(radiosondes, aircraft, surface stations, ships, buoys, TOVS
radiances and cloud drift winds from GOES satellites), and will
include middle atmosphere data from satellites (i.e. MLS, HRDI,
SWIFT ).
This work is one of two projects that comprise
MSC's
Middle Atmosphere Initiative . It is also a part of the
Global Chemistry for Climate (GCC) project.
Chemical Data assimilation.
CMAM is a comprehensive climate model with fully interactive
chemistry, radiation and dynamics. Thus, in addition to assimilating
dynamical variables, we plan to assimilate chemical data from
satellites (i.e. MLS, OSIRIS) to obtain a ``best'' estimate
of ozone and related species.
Science in support of Canadian satellite instrument developers.
With a reasonable depiction of the atmospheric state up to 80 km
(the top of the mesosphere), CMAM analyses would be able to
provide a background estimate for satellite retrievals. The
CMAM Data Assimilation group (CMAM-DA) is involved with the
Canadian SWIFT
(Stratospheric Wind Interferometer For Transport
Studies) instrument, and plans to assimilate wind and temperature
data when the satellite is launched in 2007.

Research
 Papers
Papers
 Courses
Courses




This site is maintained by
Saroja Polavarapu.
Last updated May 11, 2001.
 Papers
Papers
 Courses
Courses
![[Picture]](SP_lotus.jpg)


 Papers
Papers
 Courses
Courses



