Previous: Quasibiennial oscillations in sunspot numbers and stratospheric
winds Next: Instability of the relations Up: Ext. Abst.
QBO and surface air temperature response to solar activity
Labitzke and van Loon [3] demonstrated strong negative correlations
between solar activity and surface air temperature measured in
individual meteorological stations in the Northern hemisphere
for the west phase of the QBO. Fig.4 and 5 present the mean hemispheric
temperatures in the Northern and Southern hemispheres [14] for
local winter (January and July, respectively) for west and east
phases of QBO.
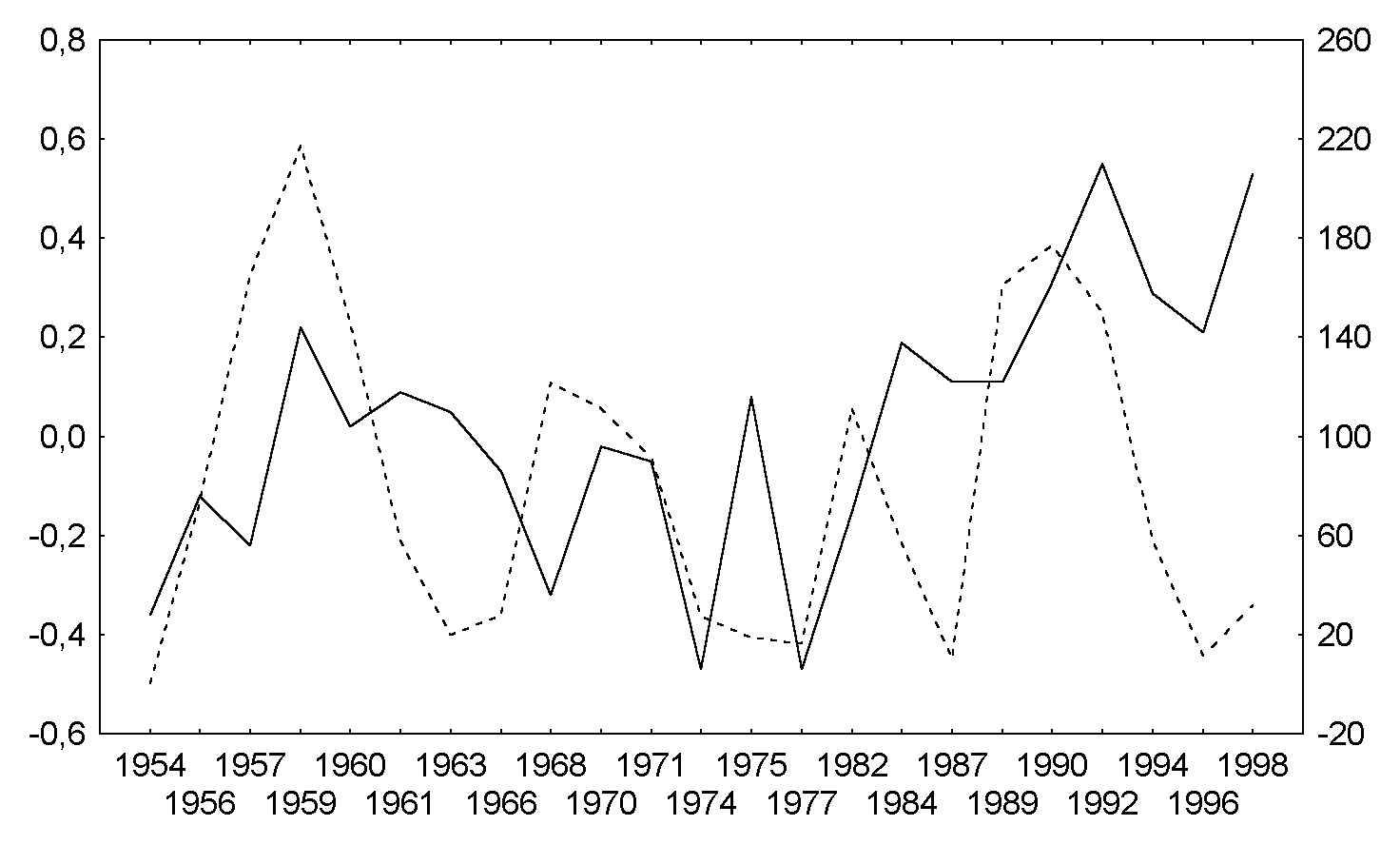
Fig.4a. Northern hemisphere, January, QBO west.
Solid line - surface air temperature; broken line - sunspot numbers
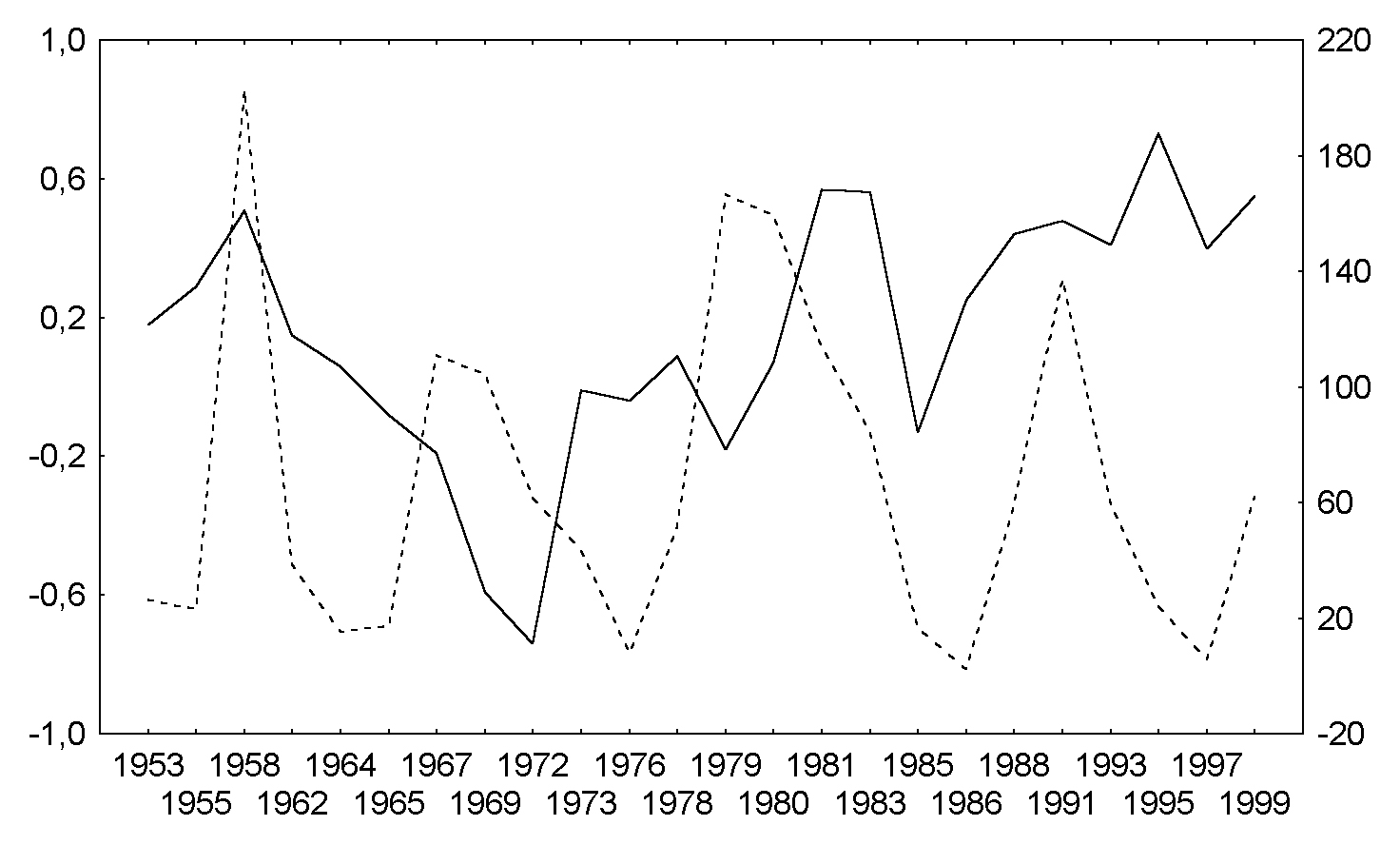
Fig.4b. The same as Fig.4a for Northern hemisphere, January, QBO east
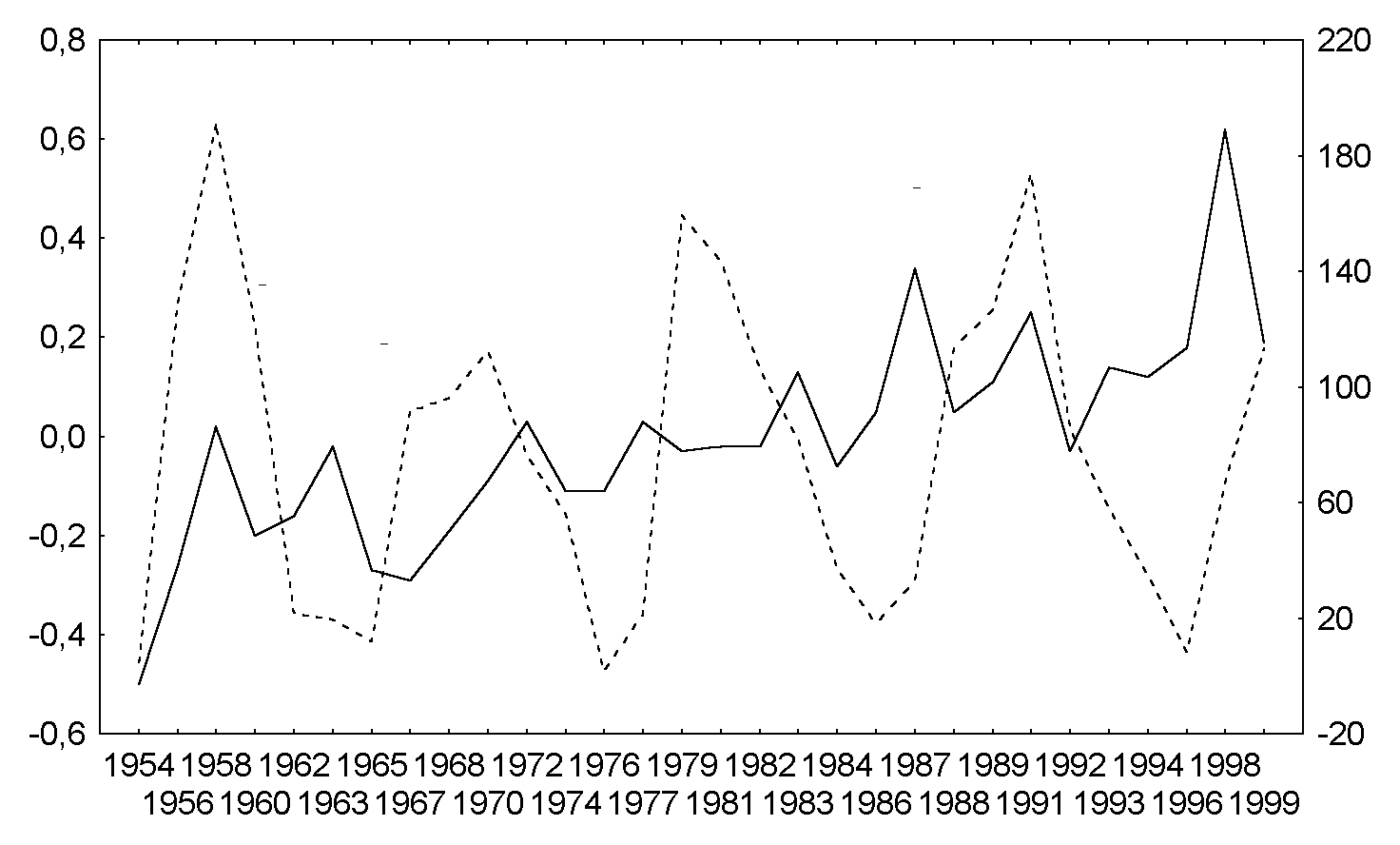
Fig.5a. The same as Fig.4a for Southern hemisphere, July, QBO west
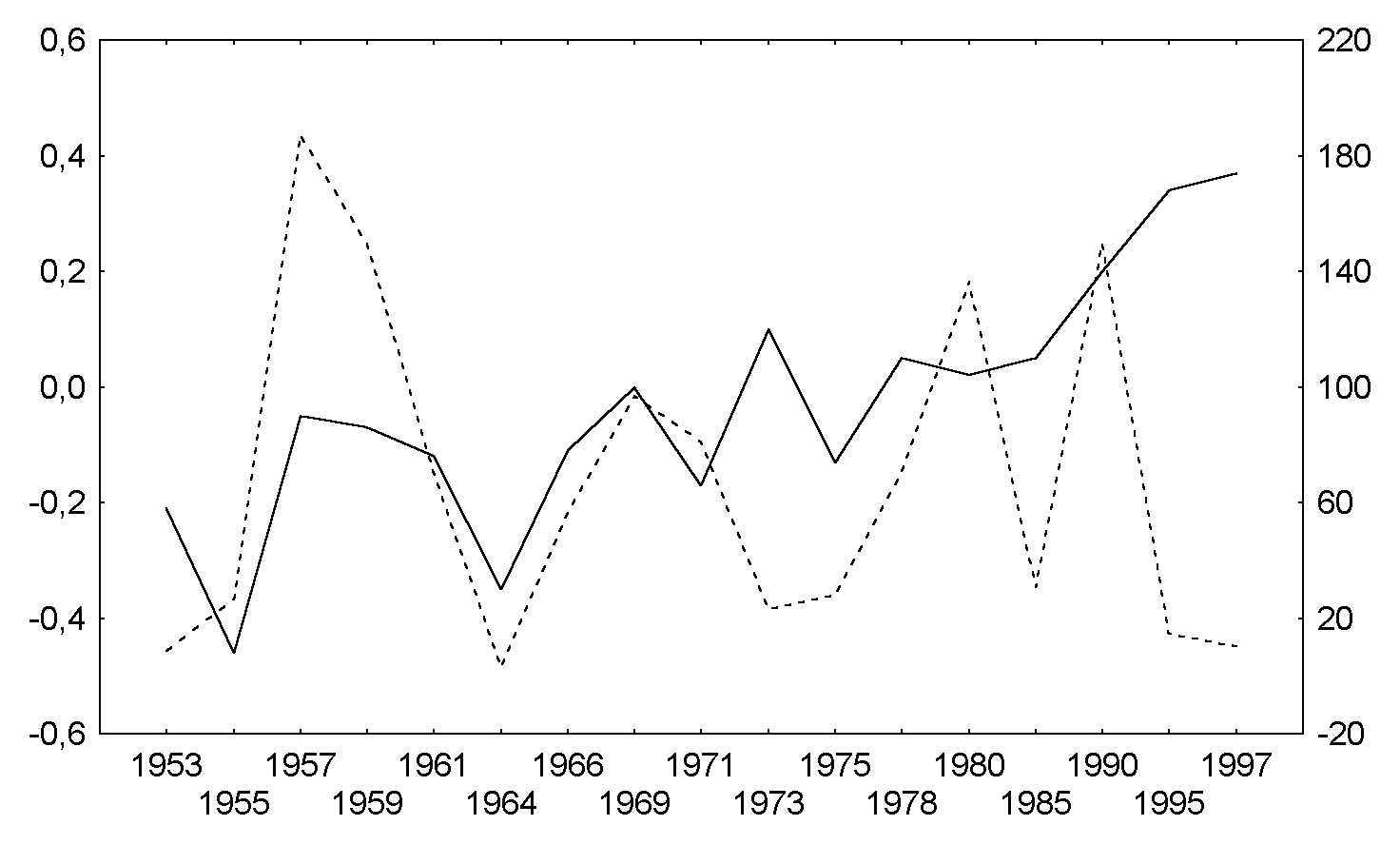
Fig.5b. The same as Fig.4a for Southern hemisphere, July, QBO east
No good correlations can be seen like the ones presented in [3].
The explanation could be that the response is not the same in
the whole hemisphere, so ne
For the west phase, statistically significant correlations (p<0.05)
were found only in the low latitude zone (± 23.6o), and only in two periods - from May to July and from October
to December - Fig.6a. The correlation is positive and in Spring-Summer
it persists for all three months even if only in May QBO is in
the west phase.
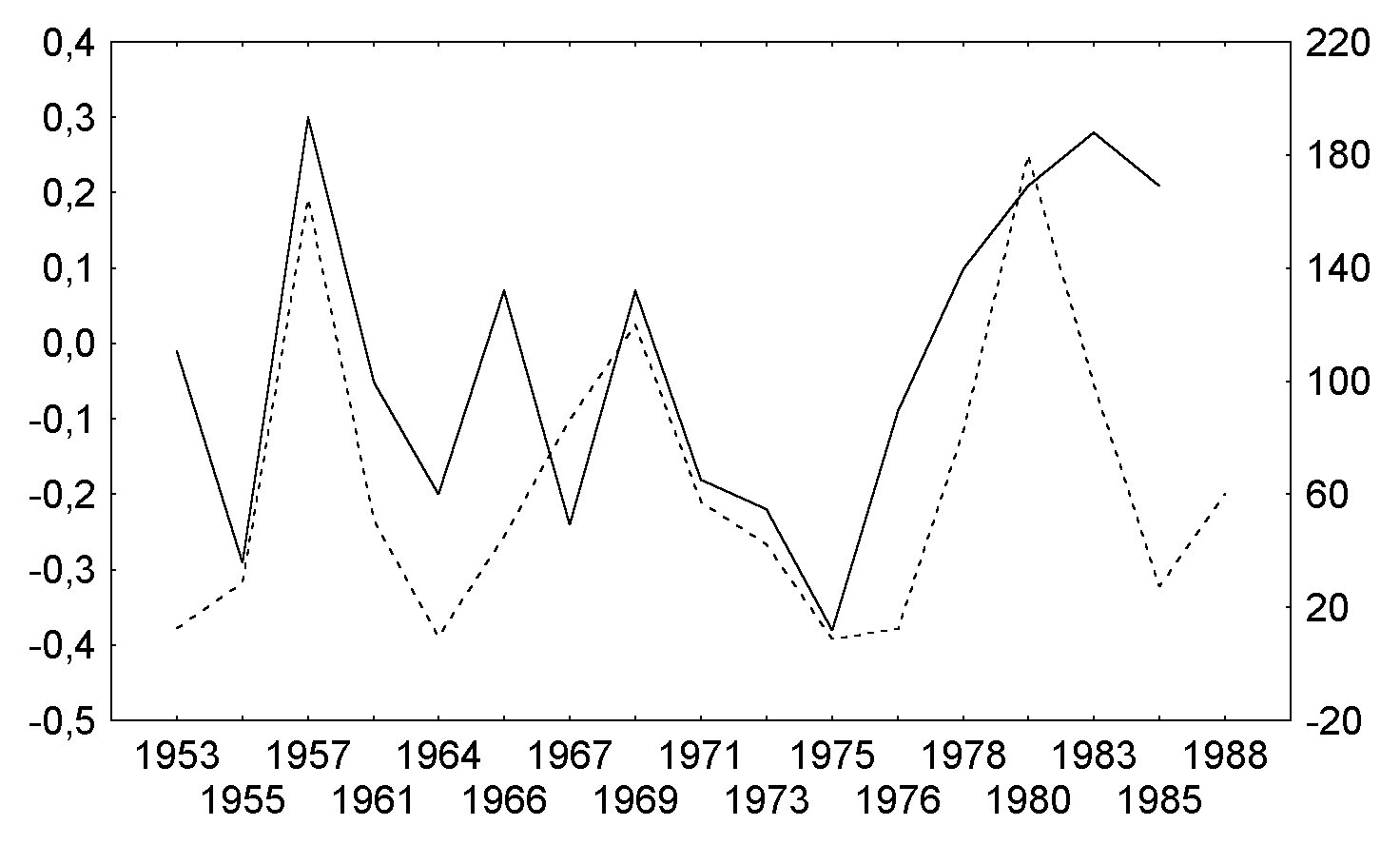
Fig.6a. May surface air temperature (solid line) and sunspot numbers
(broken line) for
the latitudinal zone 0-23.6o N, for QBO west
For the east QBO phase, statistically significant correlations
between surface air temperature and solar activity are observed
only at high latitudes (>64.2o) from December to April: negative in December, January and April
(fig.6b) and positive in February.
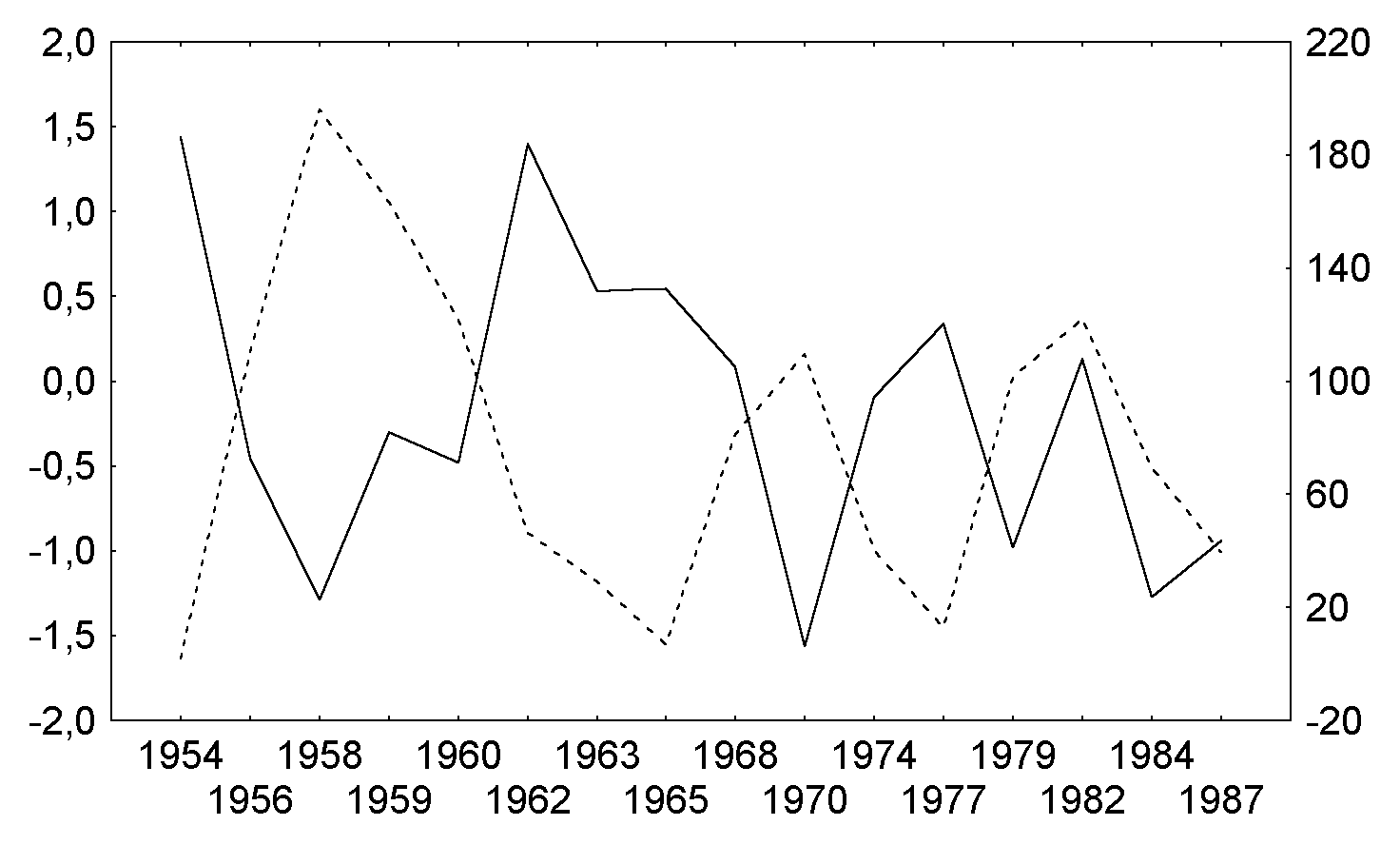
Fig.6b. April surface air temperature (solid line) and sunspot numbers
(broken line) for
the latitudinal zone 77-90o N, for QBO east
Previous: Quasibiennial oscillations in sunspot numbers and stratospheric
winds Next: Instability of the relations Up: Ext. Abst.





